
Why is an Echocardiogram Performed
An echocardiogram is a test performed on the heart using sound waves to look for any underlying cardiac issues. It is commonly used to measure the size and function of the heart’s chambers, analyse the behaviour of the heart’s valves, and measure heart muscle contraction and blood flow.
The test results provide valuable data that help cardiologists do the following:
Although echocardiograms are primarily diagnostic tests used to assess the structure and function of the heart in patients with symptoms, they can also be used as a screening tool in some cases. Therefore, your cardiologist may recommend that you undergo an echocardiogram even if you do not have symptoms of heart conditions.
Who May Need an Echocardiogram
People with one or more of the following symptoms may require an echocardiogram:
Additionally, patients with one or more of the following suspected or known conditions may require an echocardiogram:
At Capital Heart Centre, Dr Joshua Loh, our experienced cardiologist in Singapore, will thoroughly assess your condition to help you determine if an echocardiogram is suitable for you. In addition to echocardiograms, a wide variety of other tests are also available. This ensures you will undergo the right test(s) for your cardiovascular condition.
What are the Types of Echocardiograms
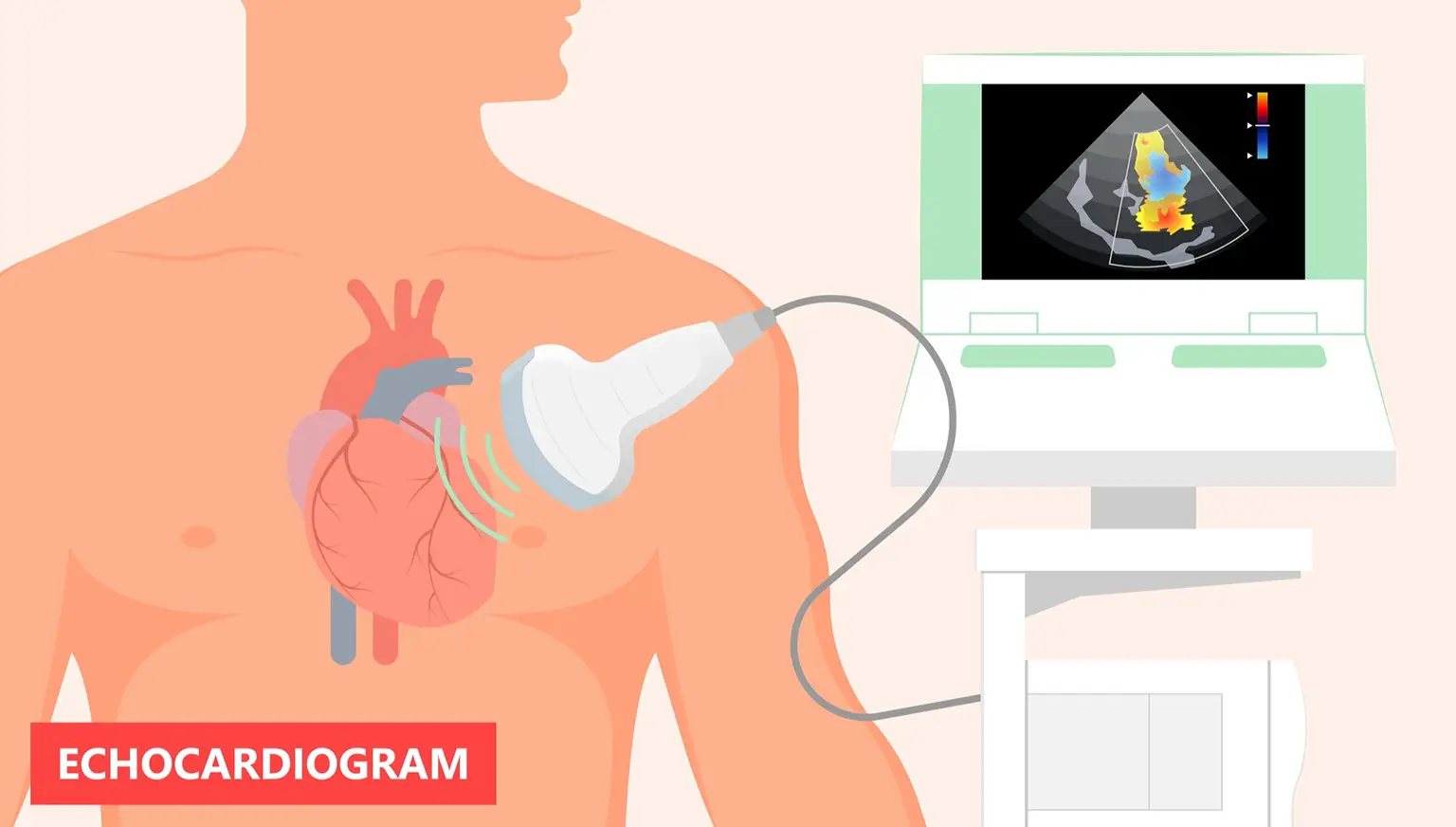
The most commonly performed echocardiogram is the transthoracic echocardiogram (TTE), a type of ultrasound scan. In TTE, a small, handheld device known as an imaging probe is positioned on the chest by your cardiologist or technician, emitting sound waves that pass through the chest cavity. As these waves encounter the heart and nearby organs, they reflect as echoes. These are captured and transformed into images of the heart in motion.
Since no imaging equipment enters the body during a TTE, it is considered a safe, non-invasive procedure.
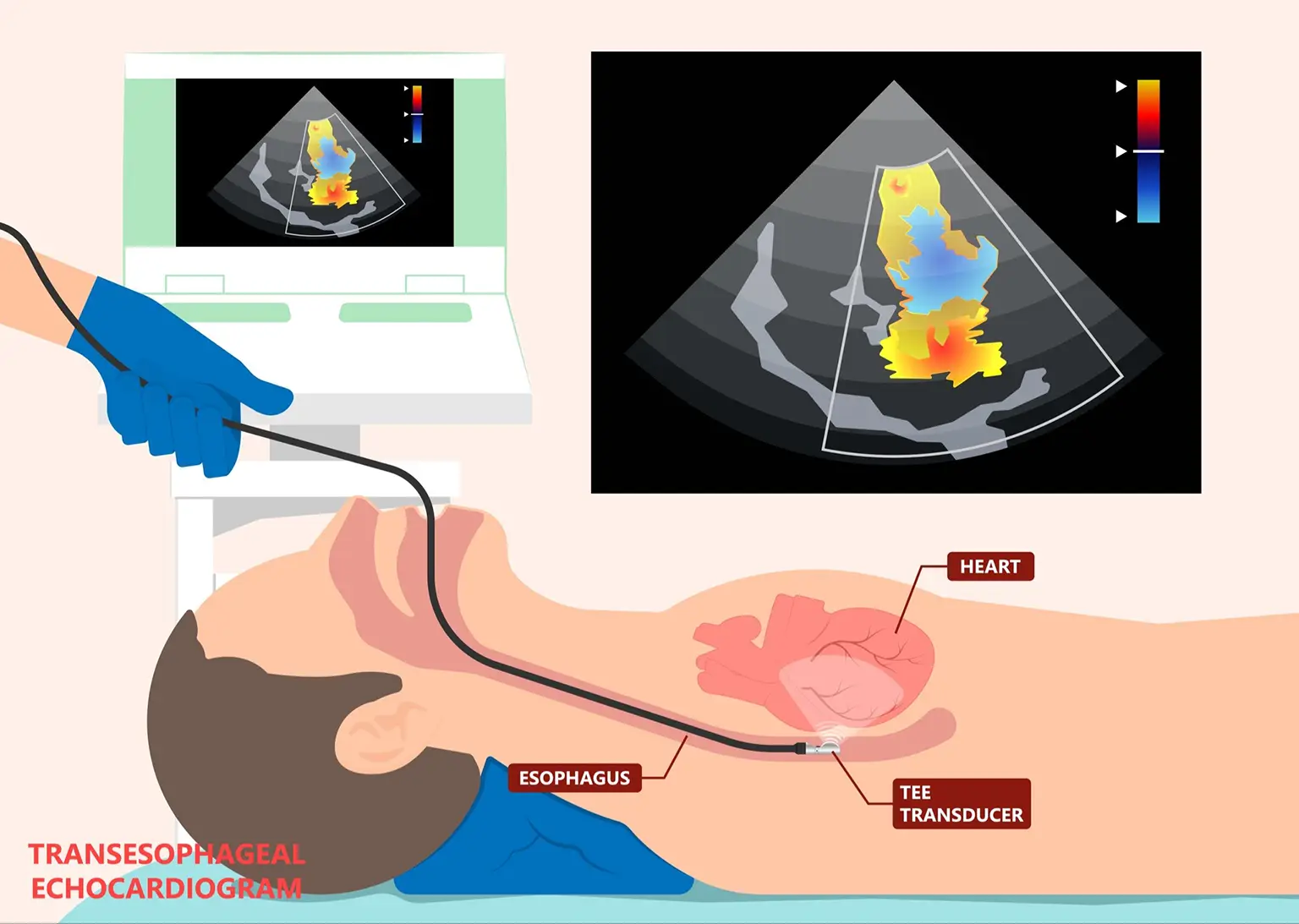
A transoesophageal echocardiogram is performed when a transthoracic echocardiogram cannot provide sufficient quality data, and better image definition is required for certain structures within the heart.
A transoesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) is done to examine the heart from inside the body. A small flexible imaging probe (a tube equipped with a sound wave emitter) is placed inside the oesophagus. The sound waves bounce off different areas of your heart, sending echoes to a computer to be turned into pictures. These pictures show the structure and function of your heart in greater detail.
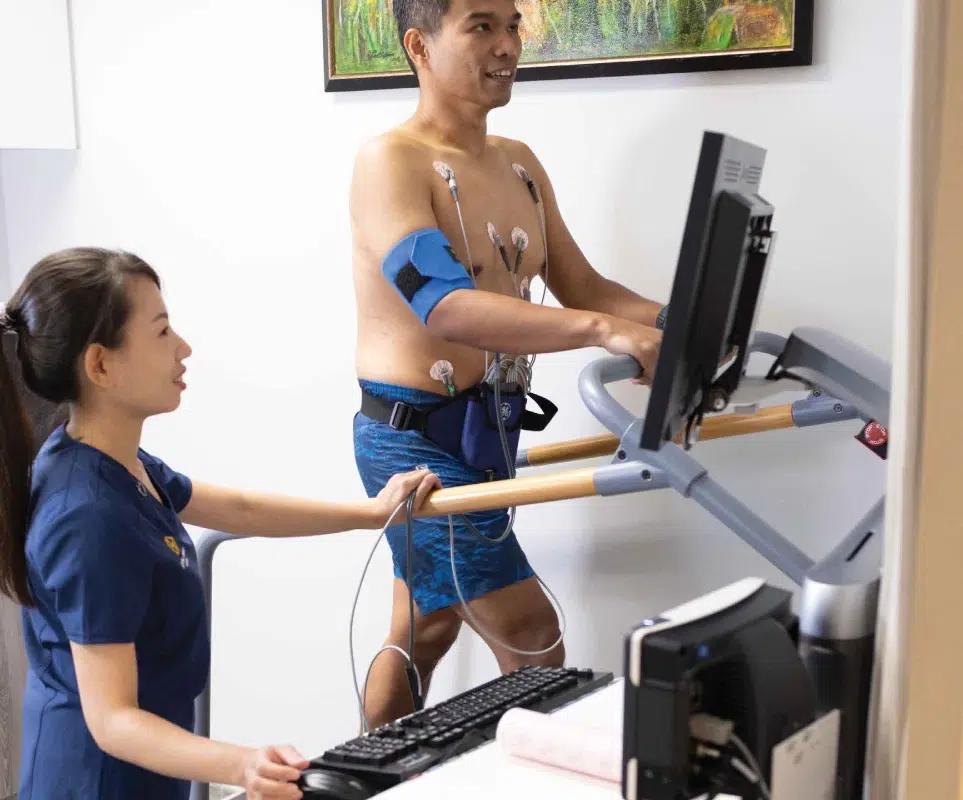
Usually performed when we suspect coronary artery disease based on a patient’s symptoms and signs. Exercise stress echocardiography combines an echocardiogram with a treadmill exercise ECG test to check how the heart responds to physical activity or stress. Ultrasound images of the heart are taken before and after exercising on the treadmill. During exercise, blood pressure and ECG is continuously being monitored. If you cannot exercise, you may be given some medication to make your heart work harder.
How the Cardiologist Decides Which Echocardiogram You Need
When a cardiologist determines which type of echocardiogram you need, they’ll base their decision on your symptoms, medical history, and the suspected heart condition. Here’s how they approach this:
How to Prepare for the Procedure

Food, Medications, and Other Preparations
Before an echocardiogram, you should let your cardiologist know if you are taking any medication, including aspirin, blood thinners, and mineral supplements. Here is a general guideline:
Important Note: The information above is meant as a general guide. Since every patient is different, it’s always best to check with your cardiologist about whether you need to adjust your medications before your scheduled echocardiogram test.
At Capital Heart Centre, a cardiology clinic in Singapore, Dr Joshua Loh will give you personalised advice on how to prepare for your tests.
What to Expect
What Would Happen During the Procedure?
What the Echocardiogram Data May Show
Heart Defects
Echocardiogram data can reveal irregular linkages between your heart and blood vessels or between the four chambers of your heart. These are usually related to congenital heart defects.
Damages to the Heart Muscles
Images from an echocardiogram may show damage to your heart tissue, which could be a sign of a past heart attack.
Various Heart Valve Problems
An echocardiogram may show any thickening or blockages inside your heart’s walls, signalling possible heart valve conditions such as stenosis (narrowing of the heart valves).
Extra tissue on your heart valves will also appear on the images, which could suggest infection or cancer.
Pump Strength
Since a TTE and TEE can accurately measure blood flow, suboptimal pump strength can be detected.
An echocardiogram will also detect if blood regurgitates back into the heart after each pump.
Changes in Heart Size
Echocardiogram data can help your cardiologist notice heart enlargement, indicating coronary artery disease and chronic high blood pressure.
Summary
| Section | Summary |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Echocardiograms are a group of non-invasive or minimally invasive tests that rely on sound waves to assess heart structure and function, identify conditions, and monitor treatment progress. |
| Who May Need It | People with symptoms like chest pain, shortness of breath, irregular heartbeats, or known heart conditions like valve disease, coronary artery disease, and heart failure. |
| Types of Echocardiograms |
|
| Preparation | Guidelines depend on the test type (TTE, TEE, Stress); they may involve fasting or avoiding certain foods/medications. |
| Procedure Experience | Generally painless, though some discomfort may occur. Stress echocardiograms may cause mild exertion discomfort. |
| Post-Procedure | Normal activities can usually be resumed after the test. Further tests may be needed based on the results |
| Results | Detects heart defects, valve issues, muscle damage, changes in heart size, and blood flow abnormalities. |
Visit Capital Heart Centre

Clear echocardiogram results can be crucial in helping cardiologists determine a correct diagnosis. Schedule an appointment with Dr Joshua Loh, Senior Consultant Interventional Cardiologist at Capital Heart Centre, which is conveniently located at Singapore’s Mt Elizabeth Novena Hospital. With more than 15 years of experience in the field of cardiology, Dr Loh is an expert in conducting detailed cardiac diagnostic and screening tests as well as executing complex coronary interventional procedures.
References
- Echocardiogram. Mayo Clinic
https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/echocardiogram/about/pac-20393856 - Transesophageal Echocardiogram. Healthline
https://www.healthline.com/health/tee-procedure

